What is an Orc Turbine and How Does It Work?
The Orc turbine is an innovative piece of technology. It converts low-temperature heat into useful energy. This process can reduce waste and improve efficiency in various applications.
Understanding how the Orc turbine works is crucial. It utilizes organic fluids for heat transfer. Unlike conventional turbines, it operates efficiently at lower heat levels. This broadens its potential use in various industries.
While the ORC system holds promise, challenges exist. Issues related to optimization and material durability need attention. Proper maintenance is crucial for its longevity and efficiency. Exploring these aspects will enhance the overall effectiveness of Orc turbine technology.
What is an Orc Turbine?
An Orc turbine, or Organic Rankine Cycle turbine, is a technology that converts low-temperature heat into mechanical energy. This process is crucial for enhancing energy efficiency. It utilizes organic fluids with lower boiling points than water. This makes it suitable for recovering waste heat from industrial processes, geothermal sources, and biomass.
According to a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Orc turbines can increase energy recovery by up to 15% in certain applications. This percentage highlights their potential impact on sustainability. However, not all systems are efficient. Some may face challenges in scaling and operation. The technology sometimes struggles with fluid selection and component durability. An ideal Orc turbine should balance efficiency and cost-effectiveness, which is still a work in progress.
Additionally, the market for Orc turbines is expected to grow. The Global Market Insights report predicts a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% by 2026. Despite this growth, the industry faces hurdles. Factors like high initial investment and technology maturity can hinder adoption. Striking the right balance between performance, reliability, and costs remains critical.
The Basic Principles of ORC (Organic Rankine Cycle) Technology
The Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) technology offers a unique approach to energy generation. It utilizes organic fluids with a lower boiling point than water. This trait allows ORC systems to capture waste heat from various processes. For instance, in industrial applications, up to 30% of total energy can be wasted as heat. Such waste heat could be effectively harnessed using ORC technology.
The cycle operates through four stages: evaporation, expansion, condensation, and compression. Heat is absorbed by the organic fluid, causing it to evaporate. The vapor then expands in a turbine, converting thermal energy into mechanical energy. Recent reports show that ORC systems can achieve efficiencies ranging from 10% to 25%. This efficiency varies based on the heat source and specific system design.
While ORC technology is promising, it has challenges. Cost-effectiveness depends on the scale of implementation. Many systems have been deemed unaffordable for smaller projects. Additionally, the choice of organic fluid can impact efficiency and environmental friendliness. Some fluids may pose environmental risks if leaked. This raises questions about the long-term sustainability of certain ORC applications. Without careful planning, these systems may not be as beneficial as expected.
Components of an Orc Turbine and Their Functions
The Orc turbine comprises several essential components that work harmoniously. A key part is the turbine itself. It converts thermal energy into mechanical energy. This transformation is crucial for efficient energy production. In recent reports, turbines of this type have achieved efficiencies of up to 80%. Yet, these figures are not always replicable. Design flaws or environmental factors can affect performance.
Another critical component is the heat exchanger. It facilitates heat transfer between the working fluid and the heat source. Efficient heat exchange is vital for maximizing energy output. However, materials used in heat exchangers can degrade, impacting long-term efficiency. Regular maintenance is necessary to prevent such issues.
Lastly, the system includes the working fluid, usually an organic compound. This fluid undergoes phase changes to generate power. While organic fluids are effective, finding the right balance of properties can be challenging. Developers must consider factors like boiling point and viscosity. Variations in these properties can lead to less-than-ideal performance. Overall, the components of an Orc turbine are interconnected. Each plays a pivotal role, but their efficacy is constantly influenced by external conditions and material performance.
What is an Orc Turbine and How Does It Work? - Components of an Orc Turbine and Their Functions
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Evaporator | Converts the working fluid into vapor using heat energy. |
| Expander | Extracts energy from the vapor, converting it into mechanical work. |
| Condenser | Condenses vapor back into liquid, releasing heat energy. |
| Pump | Circulates the working fluid from the condenser to the evaporator. |
| Heat Exchanger | Transports heat energy from the heat source to the working fluid. |
The Process of Energy Conversion in an Orc Turbine
An Orc turbine, or Organic Rankine Cycle turbine, converts low-temperature heat into mechanical energy. It uses organic fluids with a lower boiling point than water. This allows for efficient energy extraction from various heat sources, including industrial waste, solar energy, or geothermal heat.
Energy conversion begins when heat is applied to the organic fluid. The fluid vaporizes and expands, rotating the turbine. As the turbine spins, it generates electricity. The vapor is then cooled and condensed back into a liquid state. This cycle can repeat continuously, making it a viable renewable energy solution.
Tips:
- Choose a heat source with stable temperatures. This helps maintain efficiency.
- Regular maintenance of the turbine is also crucial. Check for leaks and wear over time.
- Small issues can impact performance significantly.
- Be mindful that not all heat sources are suitable for Orc turbines. Evaluate local conditions carefully before implementation.
Applications and Benefits of Orc Turbines in Renewable Energy
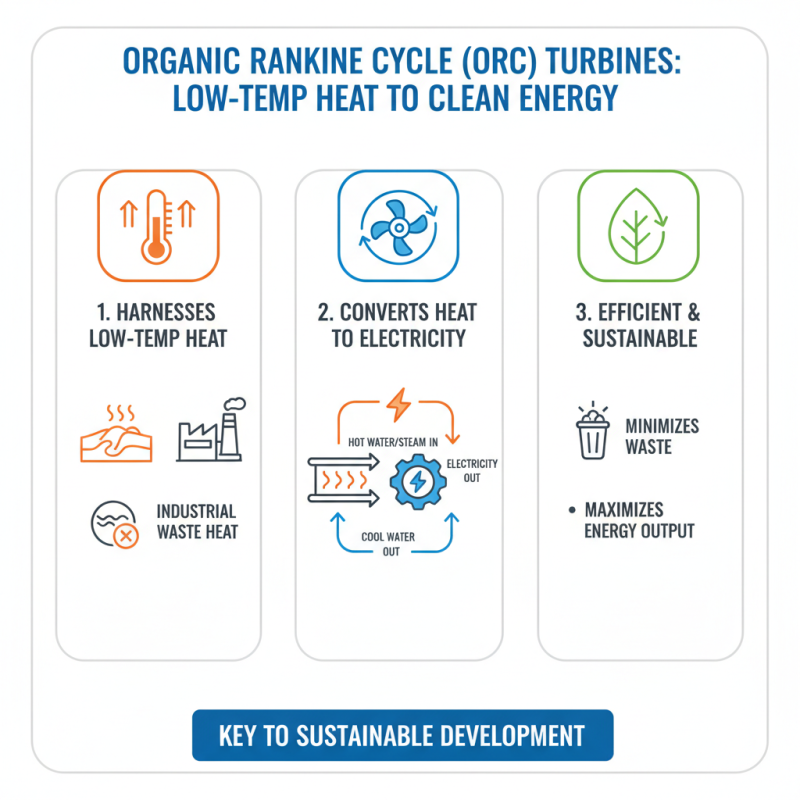
Orc turbines are a fascinating innovation in renewable energy. They turn low-temperature heat sources into clean, usable energy. These turbines are ideal for various applications, from geothermal plants to waste heat recovery systems. The efficiency of Orc turbines lies in their ability to convert hot water or steam into electricity. This process minimizes waste and maximizes energy output, making it a valuable asset for sustainable development.
The benefits of Orc turbines are significant. They can reduce carbon emissions, promoting a greener environment. With rising energy demands, Orc turbines provide an alternative that can help alleviate pressure on traditional power sources. Moreover, they can utilize heat that would otherwise be lost, making them a pragmatic choice for industries. Yet, there are challenges to consider. The initial setup costs can be high, and not all locations are suitable for Orc technology. Some installations may struggle with efficiency in fluctuating conditions. As the technology evolves, ongoing reflection on these hurdles is crucial.
Related Posts
-

Why Choose Geothermal Systems for Sustainable Heating and Cooling Solutions?
-

Why is Heat Pump Efficiency Important for Homeowners?
-
2025 Top Gas Heat Pump Innovations: Efficiency, Savings, and Sustainability
-

Best Heat Pump Contractors for Home Installation and Repair?
-
2025 Guide: How to Choose the Best Heat Pump Contractors
-

Top 10 Spa Heat Pumps for Energy Efficiency and Optimal Performance

